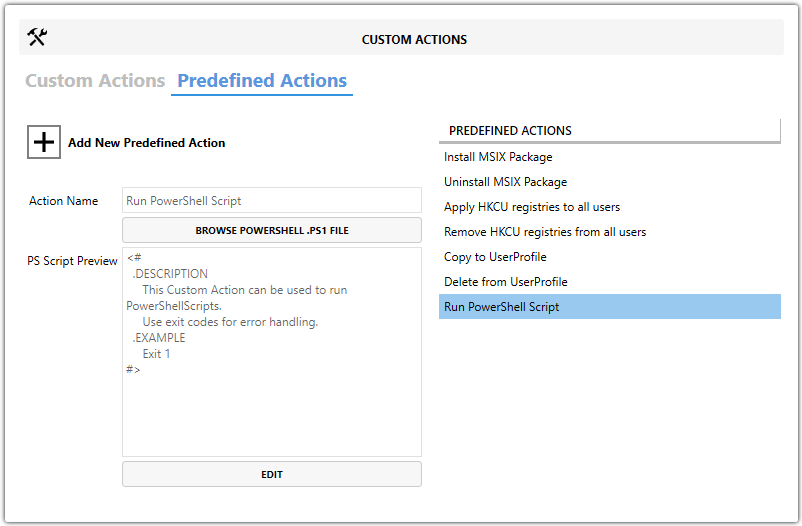
Run PowerShell Script
💎 Master Packager Pro feature
About
This is custom created predefined action by Master Packager team that can run PowerShell scripts for additional configuration and flexibility during installation.
The script runs under SYSTEM privileges, which allows it to perform tasks that a regular user might not have permission to do. The working directory during script execution is typically C:\Windows\System32, so absolute paths are recommended if your script depends on specific file locations.
PowerShell scripts executed this way can perform tasks such as:
- Creating or deleting files
- Adjusting permissions
- Modifying registry keys
- Setting environment variables
- Handling custom installation logic not possible through standard MSI tables
Note: Always ensure your script returns the correct exit code. An exit code of
0indicates success, while any other code will cause the MSI installation to fail. You can also write output to standard output to include messages in the MSI installation log.
When to Use It?
Use this predefined action when you need to:
- Run custom PowerShell logic during installation or uninstallation.
- Perform advanced system configurations.
- Automate tasks that MSI tables cannot handle directly.
How to use it?
-
Open MSI/MST with Master Packager
-
Click on Custom Actions in left menu
-
Click on Predefined Actions tab
-
Click “Add New Predefined Action” and choose “Run PowerShell Script”
-
In the Action Name field, enter a name for this predefined action.
- By default, it is “Run PowerShell Script,” but using a meaningful name helps identify your action easily.
-
To add your PowerShell code:
- Click Browse PowerShell .PS1 File to select an existing script file.
OR - Click Edit to write or paste your script directly into the editor window.
- Click Browse PowerShell .PS1 File to select an existing script file.
-
Review your script in the PS Script Preview window to ensure it’s correct.
Format should be following:
<# .DESCRIPTION This Custom Action can be used to run PowerShellScripts.
Use exit codes for error handling. .
EXAMPLE Exit 1 #>
Tip: Test your script outside of MSI first to confirm it works as expected, especially when running under SYSTEM context.