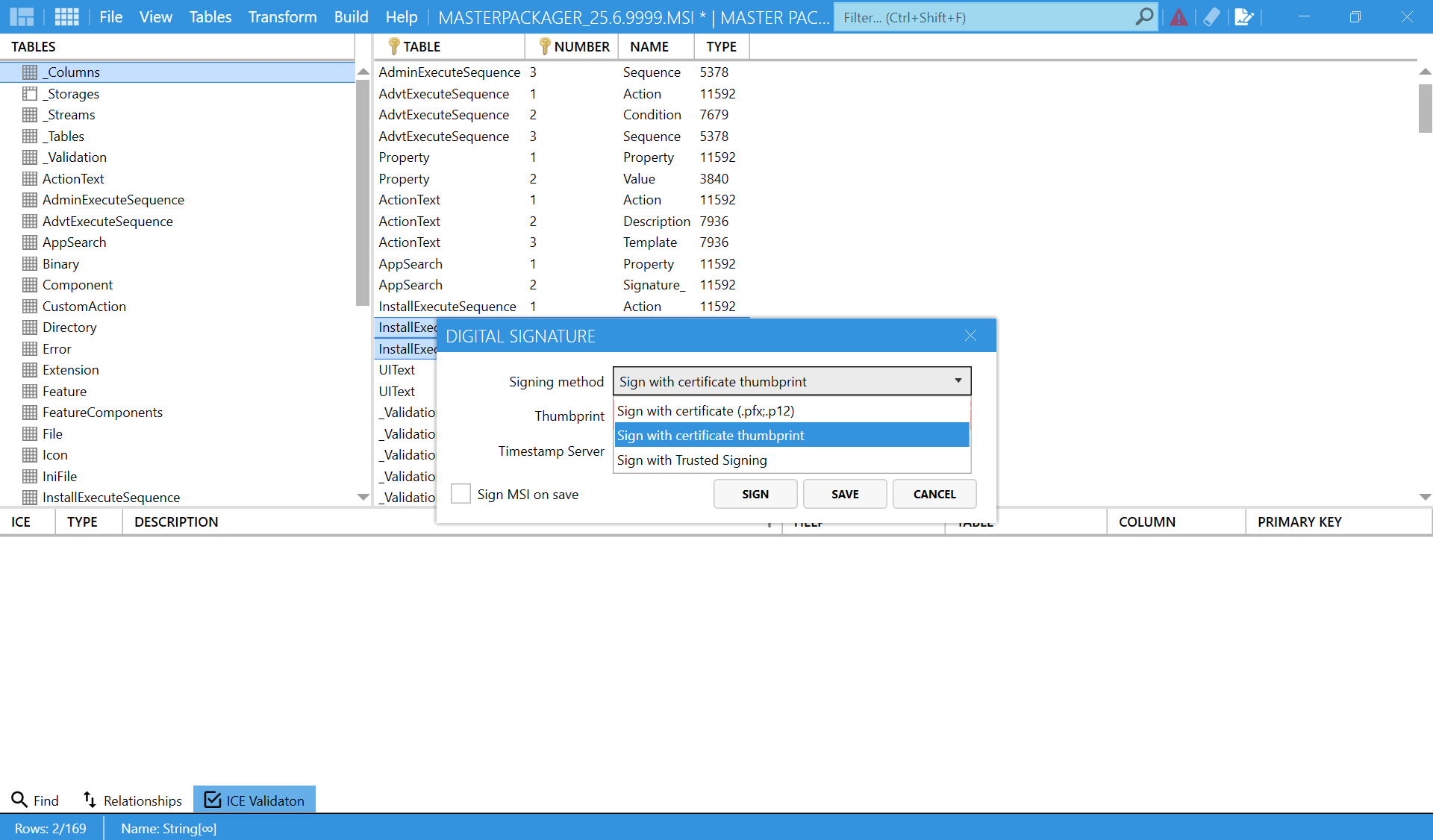
Digital Signature
💎 Master Packager Pro feature
The Digital Signature feature in Master Packager allows signing MSI files to ensure authenticity, integrity, and trust. A digitally signed package verifies that it has not been modified after signing and confirms the identity of the signer. This is an important step in securing software installations, especially in enterprise environments where unsigned packages may be blocked by security policies.
How It Works
- Applies a digital certificate to the MSI file, generating a cryptographic signature that verifies the file’s origin and integrity.
- The signature ensures that if the file is altered after signing, the digital verification will fail.
- Supports multiple signing methods, including certificate files, certificate thumbprints, and trusted cloud-based signing.
How to Use
- Open the MSI in Master Packager.
- Go to Digital Signature from the top toolbar.
- Choose a signing method:
- Sign with certificate (.pfx, .p12)
- Sign with certificate thumbprint
- Sign with Trusted Signing
- Apply the digital signature.
- Save the MSI.
The signed package will now display valid digital signature details in its file properties.
When to Use It
Use Digital Signature when:
- Preparing an MSI for internal or external distribution.
- Complying with organizational or Windows security policies that require signed installers.
- Ensuring that the package cannot be modified without detection.
For automation or continuous integration, use Trusted Signing with Azure to sign packages without manual password entry. This approach is secure and supports cloud-based authentication.