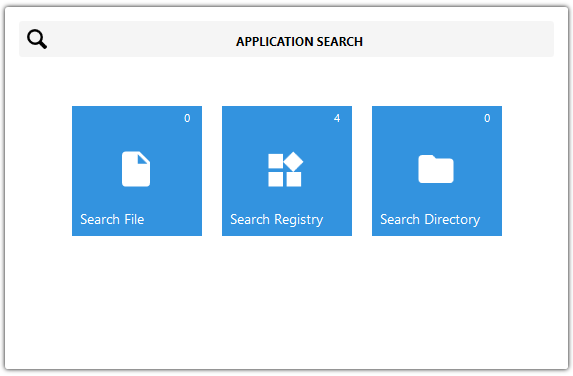
Application Search
Application Search view shows all Application Search Signatures that are in the MSI and return specific PROPERTY value. Application Search is useful feature when it is needed to get specific file, registry or directory path that is required for MSI configuration.
By clicking on a Application Search open Application Search editing flyout view.
There are 3 types of Application Search - File, Registry and Directory.
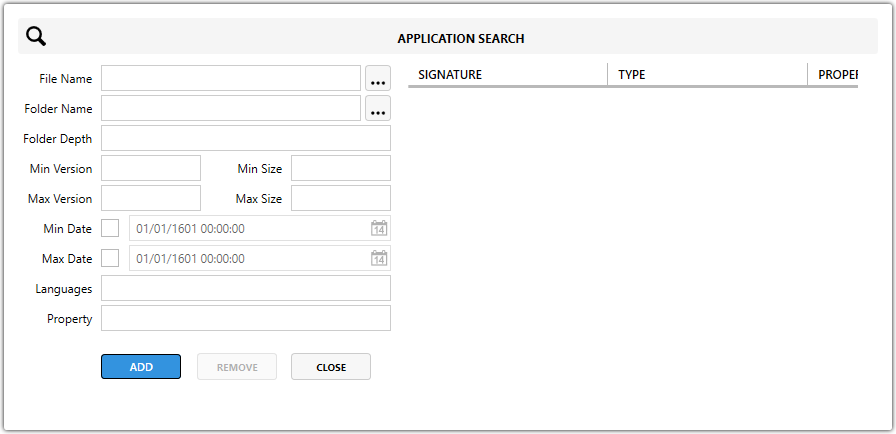
File Application Search
Used to locate a specific file on the system.
-
Searches defined folders, such as
ProgramFilesFolder, for a specific filename. -
If the file is found, the full path is saved into the specified PROPERTY.
-
Useful for detecting installed applications by checking for known executable files.
-
File Name – The name of the file to search for (e.g.
vlc.exe). -
Folder Name – The folder to search in (can be a known MSI folder like
[ProgramFilesFolder]or a custom path). -
Folder Depth – How many subfolders deep to search:
-
0= only the specified folder -
Higher numbers = deeper search into subfolders
-
-
Min Version / Max Version – Filters the search by file version number if needed.
-
Min Size / Max Size – Filters by file size to avoid false matches.
-
Min Date / Max Date – Searches for files modified within a specific date range.
-
Languages – Filters the search to files with a specific language attribute. Rarely used.
-
Property – The MSI property that stores the search result. This value can be used in conditions, paths, or other logic during installation.
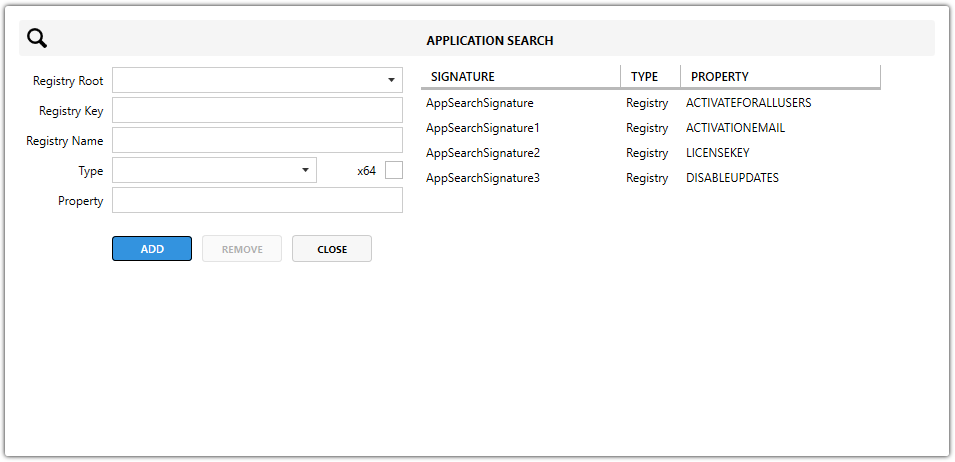
Registry Application Search
Used to locate specific registry keys or values.
-
Searches a defined registry root and path.
-
Can check whether a key exists, or read a specific value from the key.
-
Registry Root – Defines the top-level registry hive to search in.
Options include:-
HKCR– HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT -
HKCU– HKEY_CURRENT_USER -
HKLM– HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE -
HKU– HKEY_USERS -
AllUsers Dependent– Resolves to HKLM or HKCU depending on the ALLUSERS property in the MSI.
-
-
Registry Key – The path to the registry key, excluding the root.
-
Registry Name – The specific value name within the key to look up.
-
Leave empty if you want to check if the key itself exists without reading a value.
-
If filled, the value’s data will be stored in the Property.
-
-
Type – Defines the type of data to expect from the registry value.
Common types:-
REG_SZ– String -
REG_DWORD– 32-bit number -
REG_BINARY– Binary data -
REG_MULTI_SZ– Multiple strings
-
-
x64 – A checkbox indicating whether the search should look in the 64-bit part of the registry.
-
Property – The name of the MSI Property where the found registry value (or indication of existence) will be stored.
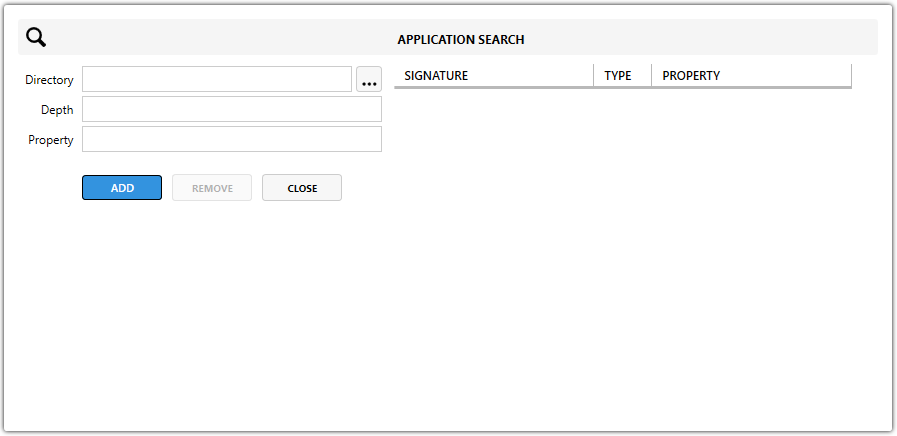
Directory Application Search
Used to verify whether a specific folder exists.
-
Searches known folders or custom paths.
-
If found, the directory path is saved into the PROPERTY.
-
Useful for checking installations that may exist in non-default paths.
-
Directory – The path of the folder you want to check. It can be a known MSI folder property like
[ProgramFilesFolder]or a custom path. -
Depth – Defines how many subfolders deep the search should go:
-
0= only the specified folder is checked -
Higher numbers search deeper subdirectories
-
-
Property – The name of the MSI Property where the found directory path will be saved. This property can be used later for installation paths, conditions, or launch conditions.
Benefits of Using Application Search
-
Helps determine if prerequisites are installed before proceeding with the MSI installation.
-
Supports creating Launch Conditions that block the install if certain applications or files are missing.
-
Allows dynamic configuration of paths, ensuring the MSI can adapt to different environments.
Note: Properties set by Application Search are preserved during repairs, ensuring consistent behavior across install, repair, and uninstall operations.