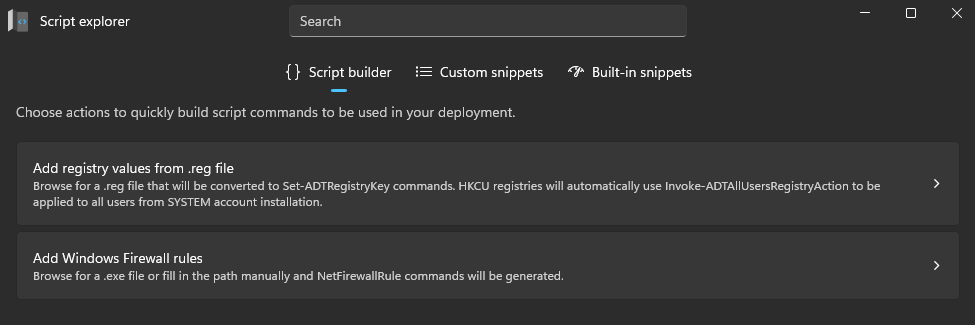
Script Explorer
The Script Explorer in Master Wrapper is a built-in tool designed to simplify working with PowerShell code inside PSAppDeployToolkit projects. It helps create, manage, and reuse script components without leaving the Master Wrapper interface.
Script Explorer is divided into three main tools, each offering different capabilities:
-
Script Builder – Generate ready-to-use PowerShell commands for common deployment tasks, such as modifying the registry or managing firewall rules, without writing code manually.
- Add registry values from .reg file – Convert
.regfiles into PowerShell commands automatically for easy integration into deployment scripts. - Add Windows Firewall rules – Create and manage firewall rules without writing
New-NetFirewallRulecommands manually.
- Add registry values from .reg file – Convert
-
Custom Snippets – Save frequently used PowerShell snippets (e.g., copy files or remove registry keys) and reuse them quickly in future projects.
-
Built-in Snippets – Access a library of predefined PowerShell structures and commands to speed up script creation and reduce errors.